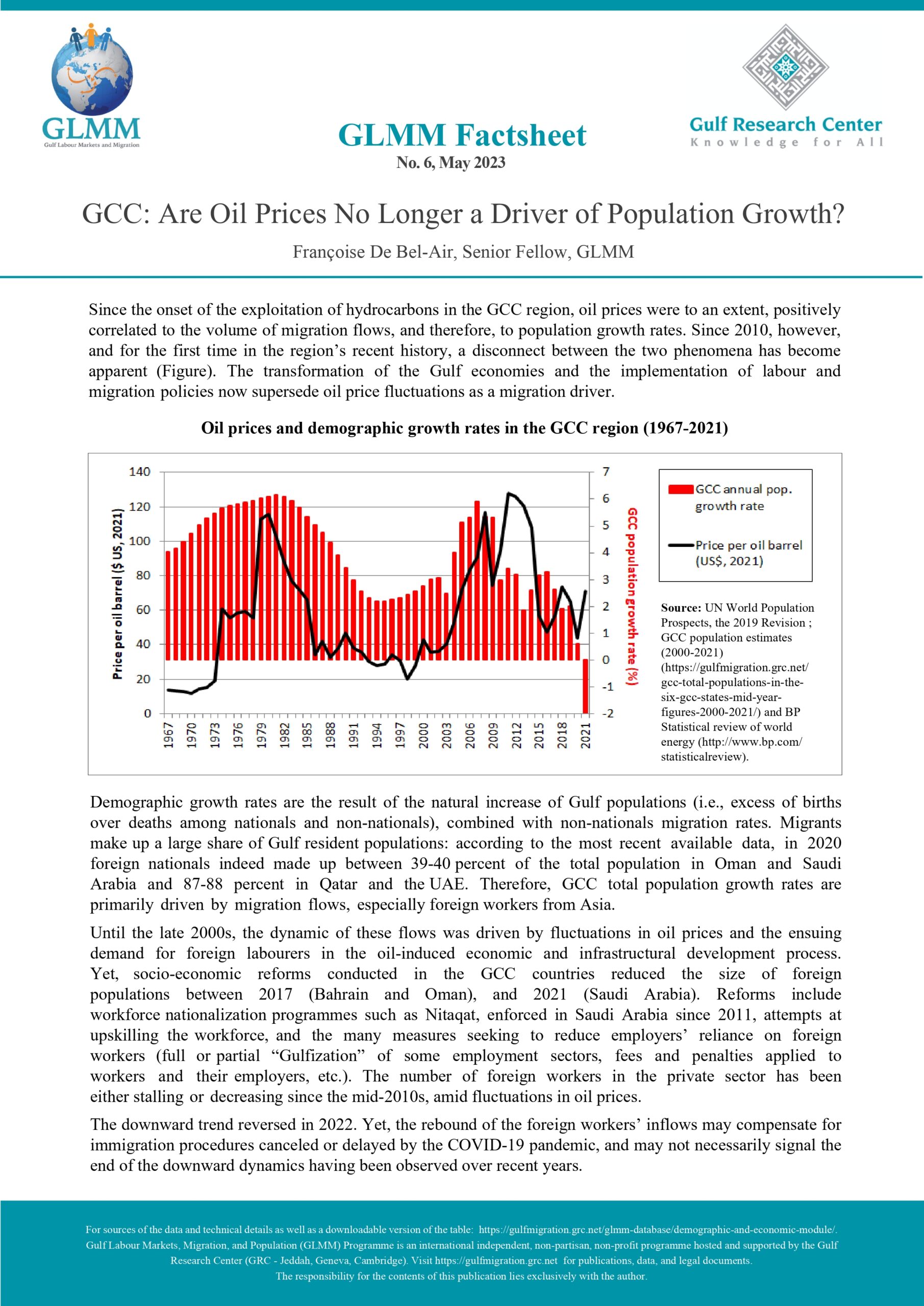
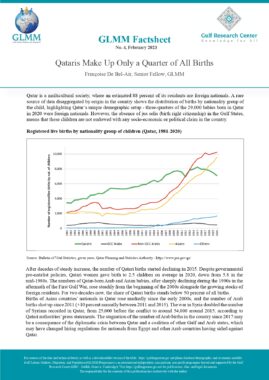
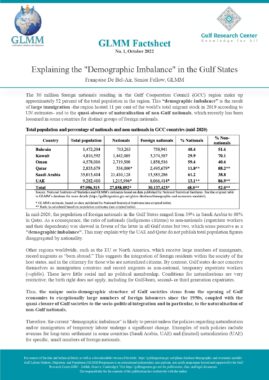
UAE: Ministerial Decision No. 360 of 1997 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of Federal Law No. 6 of 1973 Regarding Entry and Residence of Foreigners
|
Title
|
UAE: Ministerial Decision No. 360 of 1997 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of Federal Law No. 6 of 1973 Regarding Entry and Residence of Foreigners
|
|
Date of adoption
|
16 July 1997 |
|
Entry into force
|
In effect |
|
Text versions |
Arabic
Source:
|
|
Abstract
|
|
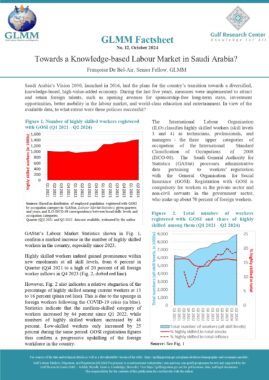
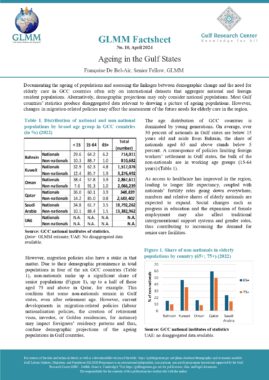
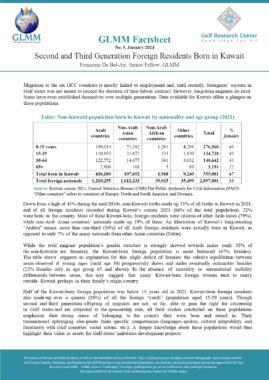
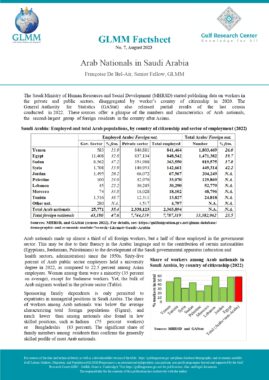
In accordance with Art. 13, a foreigner may only be granted an entry permit or visa if he meets the following conditions:
The sponsor shall commit to verifying the veracity of the information submitted on the application, bringing the sponsored person into the country and returning him to his country when necessary, as well as any other commitments imposed by the General Administration of Nationality and Residence (Art. 14). An entry permit for the purpose of work allows its holder to enter the country within two months of its issuance and remain in the country for a maximum period of thirty days from the date of entry (Art. 22). Art. 23 sets out the procedure for obtaining an entry permit for the purpose of work for each category of employer. The fourth section of the same article lists the conditions that must be met by a foreigner in order to sponsor a domestic worker. These include but are not limited to having a monthly salary of at least 6000 Dirhams, and paying a fee the equivalent of one year’s salary where the minimum salary for a domestic worker is 400 Dirhams. The following categories of foreigners may not sponsor or recruit a foreigner even if they meet the minimum salary requirement: Domestic workers and labourers (Art. 27). An entry permit for the purpose of residence may be granted to a foreigner in any of the cases listed in this article (Art. 28). An entry permit for the purpose of residence allows its holder to enter the country within two months of its issuance and remain in the country for a maximum period of thirty days from the date of entry (Art. 30). In accordance with Art. 31, a foreigner may sponsor his wife if the following conditions are met:
The foreigner may sponsor unmarried female children, as well as male children below the age of eighteen unless they are studying in one of the country’s higher education institutions. A multiple entry visa may be granted to foreigners whose work requires them to visit the country repeatedly. The visa allows its holder to enter the country multiple times within a six-month period and remain for thirty days each time (Art. 32, 33). Art. 41 lists the categories of private sector employees for whom a visit visa may be turned into a residence permit for the purpose of work. These include engineers, doctors, pharmacists, nurses, lab technicians, teachers, accountants, auditors, and others. Art. 42 sets the procedure for turning a visit visa into a residence permit for the purpose of work. Art. 43 lists categories of foreign residents of GCC countries who may enter the UAE for a visit without obtaining a visa or permit. |
|
Similar Posts:
- UAE: Ministerial Decision No. 360 of 1997 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of Federal Law No. 6 of 1973 Regarding Entry and Residence of Foreigners
- UAE: Ministerial Decision No. 360 of 1997 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of Federal Law No. 6 of 1973 Regarding Entry and Residence of Foreigners
- UAE: Ministerial Decision No. 377 of 2014 Amending Some Provisions of the Implementing Regulations of Federal Law No. 6 of 1973 Regarding the Entry and Residence of Foreigners
- Oman: Decision No. 63 of 1996 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of the Foreign Residency Law No. 16 of 1995 (copy)
- Oman: Decision No. 63 of 1996 Issuing the Implementing Regulations of the Foreign Residency Law No. 16 of 1995
Tags: Entry & Exit Conditions, Laws & Regulations, United Arab Emirates