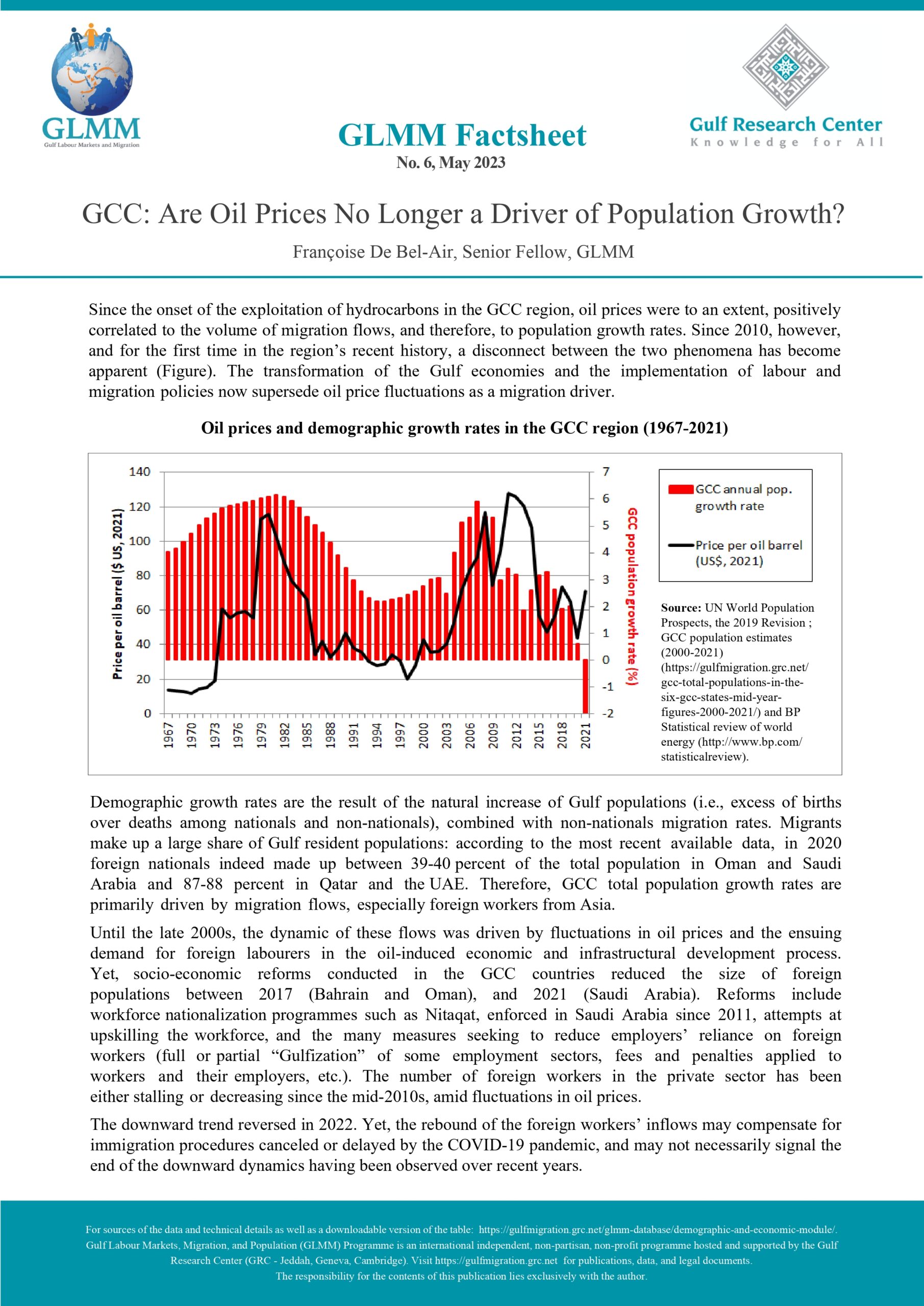
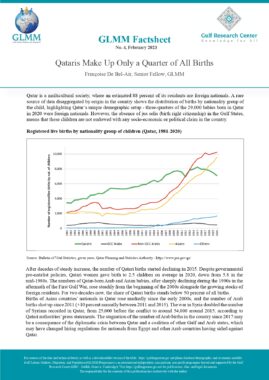
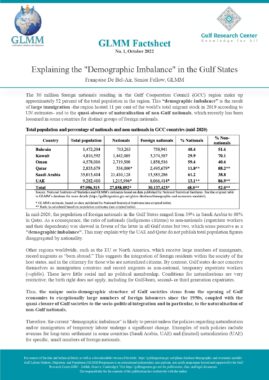
Oman: Foreigners’ Residence Law
|
Title
|
Oman: Foreigners’ Residence Law
|
|
Date of adoption
|
1995 |
|
Entry into force
|
In effect |
|
Text versions |
Arabic
Source: – Sultanate of Oman Royal Oman Police, accessed: 12 October 2014, http://www.rop.gov.om/english/roplaws.asp |
|
Abstract |
|
| Keywords: Oman, Laws & Regulations, Irregular Migration
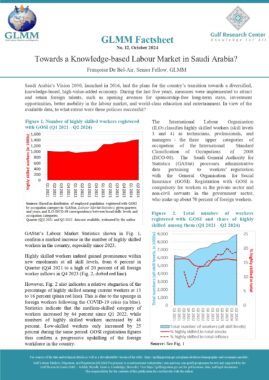
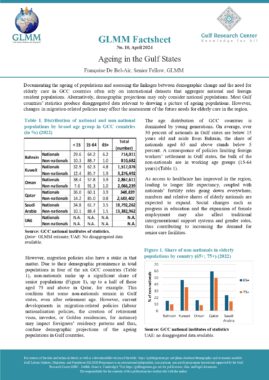
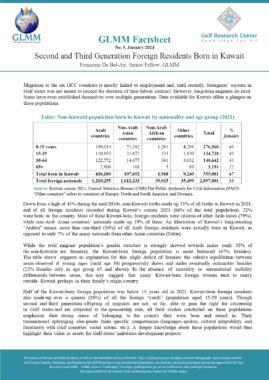
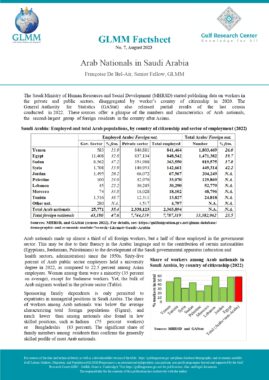
This law regulates residence of foreigners in Oman. Foreigners are defined as those who do not hold Omani citizenship (Art. 2). This law does not apply to certain categories listed in Art. 4, including citizens of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). In accordance with Art. 29, a foreigner who has entered the country illegally shall be deported at his own expense or the expense of those who facilitated his entry or employed him. Without prejudice to the terms of article 11 of this law, this foreigner may re-enter the country if he meets the conditions of article 5 (Art. 29). A foreigner shall be deported if he is sentenced to deportation for committing a crime or felony after serving any other penalty he has been sentenced to (Art. 30). Art. 31 lists the cases in which the Inspector General may order the cancellation of a foreigner’s residence. The cancellation shall extend to his spouse and any children he is supporting. A foreigner who has been issued a deportation order may remain in the country for one month, renewable once, to settle his affairs after offering a personal guarantee (Art. 33). A foreigner who has been deported may not be issued another entry visa until two years have lapsed and with a special permission from the Inspector General (Art. 34). Any foreigner who has been deported from the country shall be included on the list of unwanted persons (Art. 35). In accordance with Art. 40, the Inspector General shall issue a decision which specifies the fees for entry visas. Residence permits and transit visas. The highest fee that may be imposed shall be 50 Riyals. Chapter X of this law lists all the penalties for violating the articles of this law. |
|